Literal means whatever which is being said is meant as per the words being used. In simple words, we go by the dictionary meaning of the words
While Figurative means ‘drawing the mental picture’ of whatever is being said as it will help convey an idea faster and more vividly than literal language.
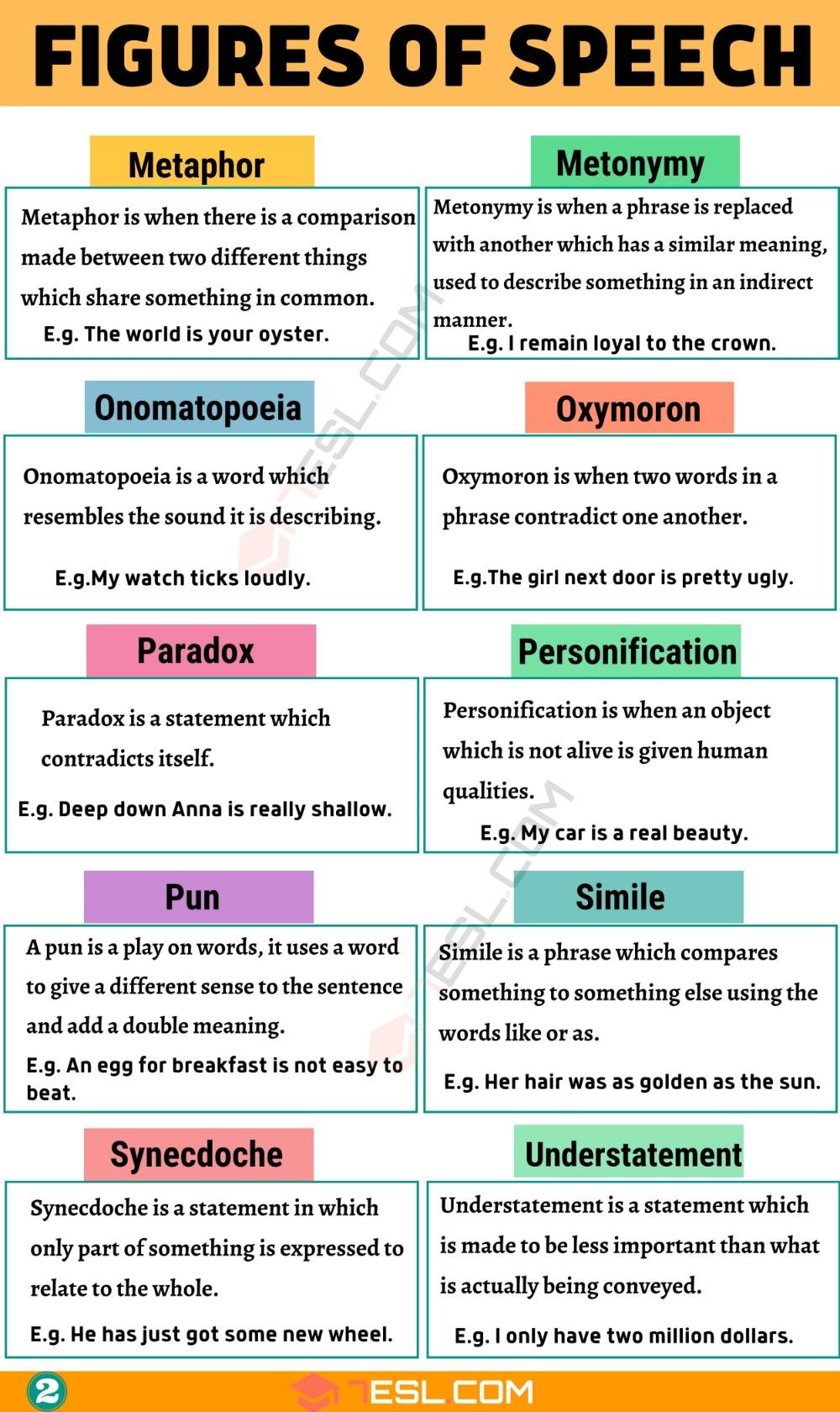
1.) Simile.
Simile is a figure of speech that uses a comparison between two different things. It is done using the words “like”, “as” or so.
These two things must have one thing in common.
2.) Metaphor
Metaphor is a figure of speech that uses a comparison between two different things. These two things must have one thing in common.
But It is done without using the words “like”, “as” or so.
3.) Personification
Personification is a figure of speech where human qualities are given to objects or ideas.
These qualities may be emotions, desires, sensations, gestures and speech.
4.)Hyperbole.
Hyperbole is a figure of speech, in which we exaggerate or overstate any statement.
It is done for expressing something forcibly and clearly.
5.)Apostrophe.
An apostrophe is a figure of speech in which some absent or nonexistent person or thing is addressed as
if present and capable of understanding.
It is an exclamatory figure of speech as an exclamation is used in it.
6.) Oxymoron.
An oxymoron is a figure of speech containing words that seem to contradict each other.
That is one word says one thing and the other word says the other thing.
7.) onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia is defined as a word which imitates the natural sounds of a thing.
That is, it is a word which emits the sound of the that thing.
Repetition and Alliteration
Repetition :
A Repetition is a figure of speech in which a word or a group of words is repeated.
It is used to create rhythm and bring attention to an idea
Let’s understand Word Repetition with an example in which a Word is Repeated.
The President said, “Work, work and Work” are the keys to success.
Here, you can see that word ‘work’ is repeted thrice to bring attention to the importance of ‘Work’ to gain success.
Now, let’s look into Figure of Speech, Alliteration
Alliteration is a figure of speech in which initial sounds of words repeat.
Lets look into examples of Alliteration.
Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers.
She sells seashells down by the seashore.
Note that alliteration is dependent on the beginning sound and not the beginning letter.
For example, “cat” is not alliterative with “choice”, but is alliterative with “kick”.
So, In Alliteration initial sounds of words are repeated.
- Synecdoche
A Synchedoche is a figure of speech that uses a part to represent a whole thing. Or it uses a whole thing to represent a part. - Metonymy
A Metonymy is a figure of speech where one thing is substituted by another thing that is closely associated with it.
or in other words, one object is being replaced by another object which is closely linked to it. - Climax
A Climax is a Figure of speech in which a series of words, phrases, or ideas are arranged in ascending order of its importance.
And In the case of a situation, all events are in sequential order. - AntiClimax
An Anti-Climax is a Figure of speech in which a series of words, phrases, or ideas are arranged in descending order of its importance.
And In the case of a situation, all events are in reverse order of their occurrence. - Antithesis
An Antithesis is a figure of speech in which two opposite ideas are put together in a sentence to achieve a contrasting effect.
It is done to put emphasis. - Epigram
An Epigram is a figure of speech in which a short witty sentence is used to express a general truth or comment.
It is a brief, clever, and memorable statement. - Pun.
A Pun is a figure of speech where we play with words that have more than one meaning.
It is used to create a humorous effect.